What is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a type of minimally invasive gallbladder surgery. Doctors use it to remove the gallbladder through small cuts in the belly. This method is also called keyhole or laparoscopic gallbladder removal surgery. Many people in the United States choose this option because it often leads to a faster recovery. The gallbladder is a small organ that stores bile, which helps digest fat. When it causes problems, removal may be needed.
Indications: When is this Surgery Needed?
Doctors may suggest laparoscopic cholecystectomy for several reasons. Most often, it is done when gallstones cause pain or infection. Sometimes, other gallbladder problems also require surgery. Common reasons include:
Usually, your doctor will run tests to confirm the need for surgery. Early treatment can help prevent serious problems.
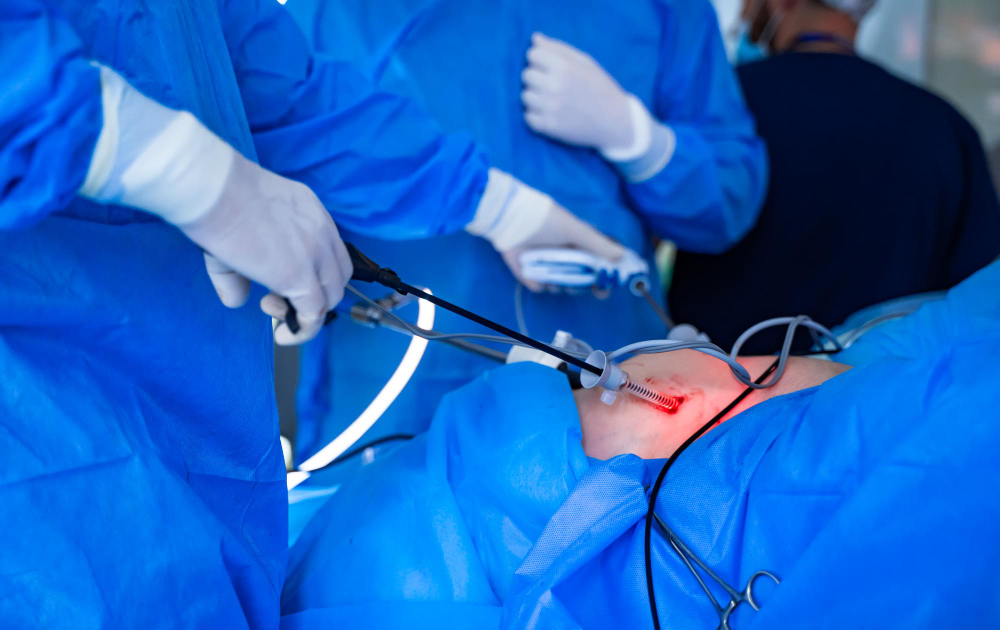
How the Procedure is Performed
First, the patient receives anesthesia to sleep during the surgery. Next, the surgeon makes a few small cuts in the belly. Through these cuts, thin tools and a camera are inserted. The camera shows the inside of the belly on a screen. Then, the surgeon carefully removes the gallbladder. After that, the cuts are closed with stitches or glue. Most surgeries take about one to two hours. Because the cuts are small, healing is often quicker than with open surgery.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
This minimally invasive gallbladder surgery offers many advantages. For example, patients often feel less pain after surgery. In addition, the hospital stay is usually shorter. Other benefits include:
Because of these benefits, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is now the most common way to remove the gallbladder in the United States.
Risks and Possible Complications
Although this surgery is safe for most people, there are some risks. Like any operation, problems can happen. Possible risks include:
However, serious problems are rare. According to the CDC, most people recover well after laparoscopic gallbladder surgery.
Recovery and Aftercare
After surgery, most people go home the same day or the next. At first, you may feel tired or sore. However, pain usually gets better within a few days. You can often return to light activities in about a week. Full recovery may take two to four weeks. During this time, follow your doctor’s instructions. For example, keep the cuts clean and dry. Also, watch for signs of infection, such as redness or fever. If you notice any problems, call your doctor right away.
Tips for a Smooth Recovery
To help your body heal, try these tips:
With good care, most people recover quickly from laparoscopic gallbladder surgery.
Prevention of Gallbladder Problems
While not all gallbladder issues can be prevented, some steps may help. For example, eating a healthy diet can lower your risk. Try to:
These habits may help keep your gallbladder healthy. Still, if you have symptoms, see your doctor for advice.
For personalized advice on laparoscopic cholecystectomy, consult Bakhetia Hospital.