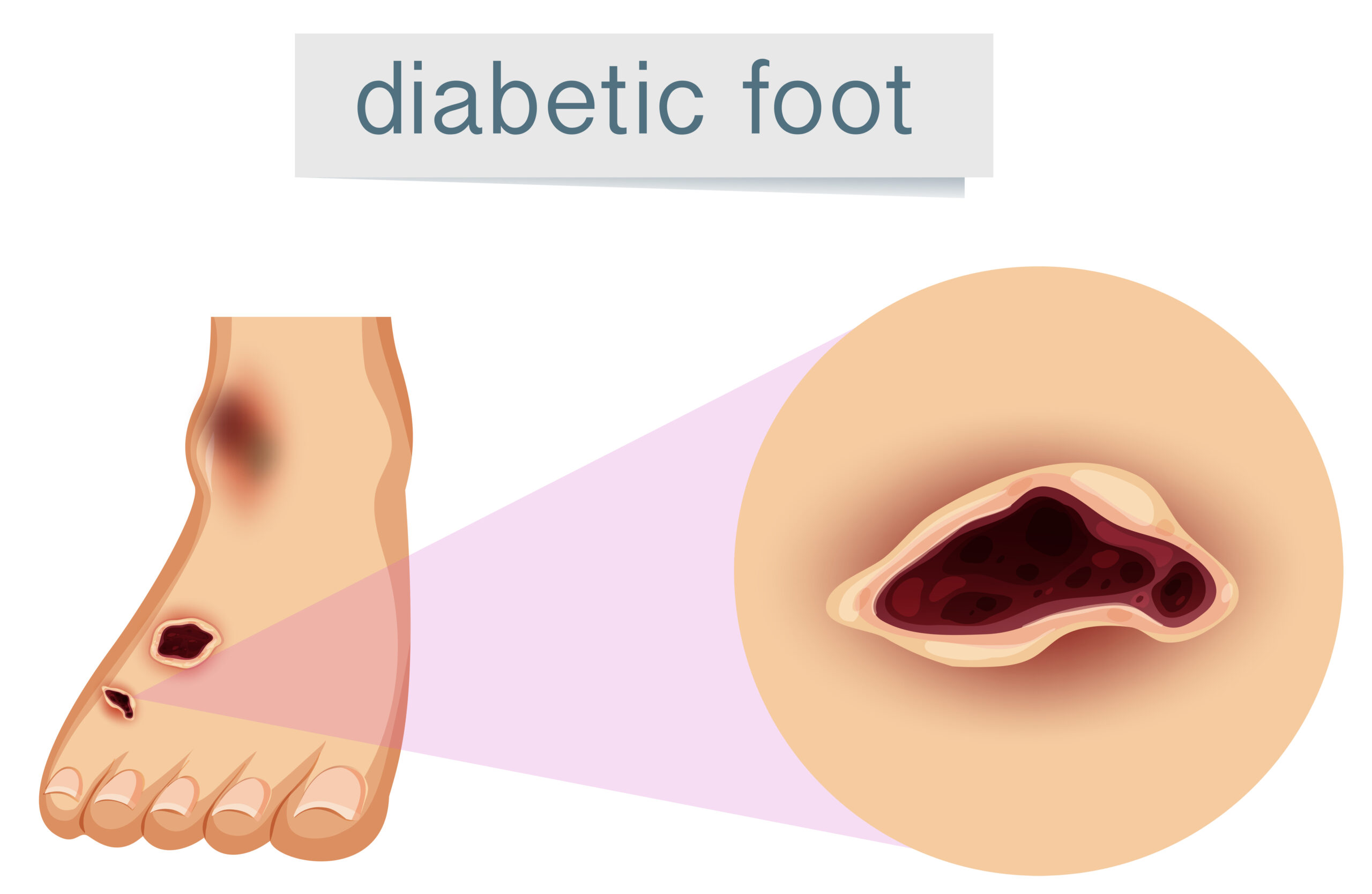
Gangrene in diabetic foot is a serious health problem for people with diabetes. It happens when body tissue dies due to poor blood flow or infection. Because diabetes can cause foot complications, gangrene is a risk if wounds or infections are not treated quickly. Early signs of gangrene, such as changes in skin color or foot infection in diabetes, should never be ignored. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for gangrene in diabetic foot can help prevent severe problems.
What is Gangrene in Diabetic Foot?
Gangrene is the death of body tissue. In people with diabetes, it often affects the feet. This happens because diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves. As a result, wounds heal slowly and infections are more likely. If blood cannot reach the foot, tissue may die. This is called gangrene. It is a serious diabetic foot complication that needs quick medical attention. Without treatment, gangrene can spread and may lead to amputation.
Common Symptoms
It is important to notice early signs of gangrene in the diabetic foot. Quick action can save tissue and prevent more damage. Watch for these symptoms:
If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical help right away. Early treatment can prevent serious diabetic foot complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can cause gangrene in diabetic foot. Diabetes can damage small blood vessels, making it hard for blood to reach the feet. This poor blood flow means wounds heal slowly. Infections can also develop easily. Here are some common causes and risk factors:
Because of these risks, people with diabetes should check their feet daily. This simple step can help catch problems early.
How is Gangrene Diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose gangrene in diabetic foot. First, they will examine your foot and ask about your symptoms. Next, they may order tests to check blood flow and infection. Common diagnostic steps include:
Early diagnosis is key. It helps doctors choose the best treatment and prevent further damage.
Treatment Options
Treating gangrene in diabetic foot depends on how severe the problem is. Doctors aim to stop the spread of tissue death and save as much healthy tissue as possible. Common treatment options include:
Doctors may also suggest blood sugar control and regular foot care. These steps help prevent future problems. According to the CDC and WHO, early treatment gives the best chance for recovery.
Prevention Tips for Diabetic Patients
Preventing gangrene in diabetic foot is possible with good daily habits. Here are some tips to lower your risk:
In some areas, local clinics offer special diabetic foot care. Ask your doctor about services in your city or region.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to seek medical help if you notice any signs of infection or gangrene. For example, if you see color changes, swelling, or wounds that do not heal, call your doctor right away. Early care can prevent serious diabetic foot complications. Do not wait for pain, as nerve damage may hide symptoms. Always follow your diabetes care plan and attend regular check-ups.
If you notice any symptoms of gangrene in your diabetic foot, consult Bakhetia Hospital immediately for personalized care.